- Static
- Dynamic
Introduction to Data Structures
Data Structures – The logical or mathematical
model of a
particular organization of data is called Data Structures.
Data Types vs Data Structures
–
| Data Types | Data Structures |
|---|---|
| Data Type is the kind or form of a variable which is being used throughout the program. It defines that the particular variable will assign the values of the given data type only. | Data Structure is the collection of different kinds of data. That entire data can be represented using an object and can be used throughout the entire program. |
| Implementation through Data Types is a form of abstract implementation. | Implementation through Data Structures is called concrete implementation. |
| Can hold values and not data, so it is data less. | Can hold different kind and types of data within one single object. |
| Values can directly be assigned to the data type variables. | The data is assigned to the data structure object using some set of algorithms and operations like push, pop and so on. |
| No problem of time complexity. | Time complexity comes into play when working with data structures. |
| Examples: int, float, double etc. | Examples: stacks, queues, tree etc. |
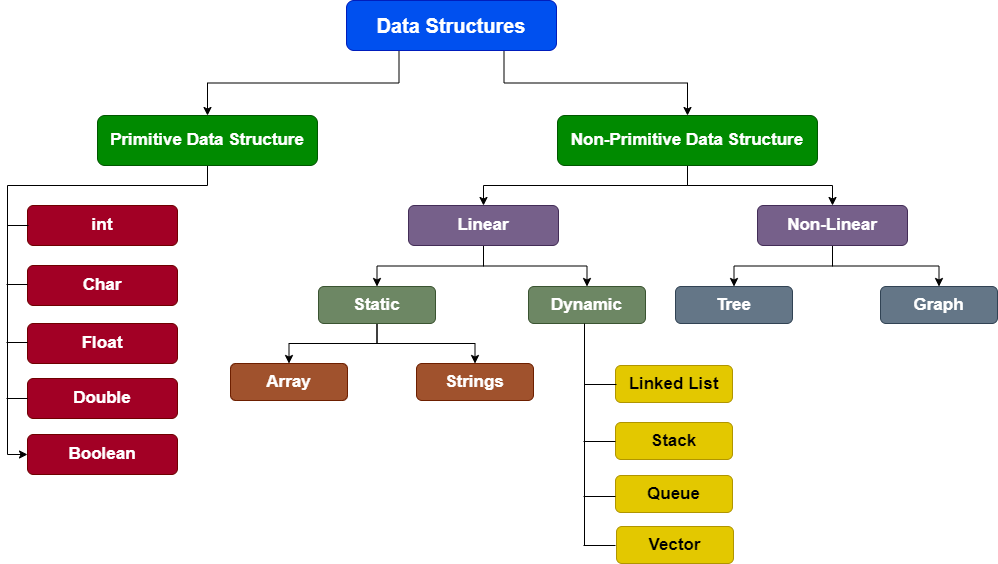
Types of Data Structure
–
- Primitive
- Non-Primitive
Primitive Data Structure
– Those basic data structures which are pre-defined in standard library. It can store the
value of
only one
data type. It cannot contain null values. ie – int, char, float etc.
Non-Primitive Data Structure
– Those data structures which are user-defined (except strings) which can be easily
created
or
modified by
user. They can store multiple values and invoke methods to perform certain operations. ie –
string,
array
etc.
Linear Data Structure
– In linear data structure data is organized in sequential order.
Types of linear Data Structure
–
Static Data Structure
– A static data structure is an organization or collection of data in memory which have a
fixed
size,
that is, it can store a limited amount of elements or data in it. ie – array, string.
Dynamic Data Structure
– A dynamic data structure is an organization or collection of data in memory which do not
have a
fixed size, that is, its size can be modified during the operations performed on it and can store a
variable
amount of elements or data in it. ie – linked list, queue, stack etc.
Types of Dynamic Data Structure –
- Linked list
- Stack
- Queue
Non-linear Data Structure
– In non-linear data structure data is organized in random order.
Types of non-linear data structures
- Trees
- Graphs
- Heaps
- Tries
- Maps
- Dictionaries
Difference between linear and non-linear data structure
–
| Linear Data Structure | Non-Linear Data Structure |
|---|---|
| In a linear data structure, data elements are arranged in a linear order where each and every element is attached to its previous and next adjacent. | In a non-linear data structure, data elements are attached in hierarchically manner. |
| In linear data structure, single level is involved. | Whereas in non-linear data structure, multiple levels are involved. |
| Its implementation is easy in comparison to non- linear data structure. | While its implementation is complex in comparison to linear data structure. |
| In linear data structure, data elements can be traversed in a single run only. | While in non-linear data structure, data elements can't be traversed in a single run only. |
| In a linear data structure, memory is not utilized in an efficient way. | While in a non-linear data structure, memory is utilized in an efficient way. |
| Applications of linear data structures are mainly in application software development. | Applications of non-linear data structures are in Artificial Intelligence and image processing. |
| ie – array, stack, queue, linked list, etc. | ie – trees, graphs, heaps, dictionaries, tries, maps etc. |